Page History
...
- At its core, the EWA algorithm looks at the cell-to-cell delta in source to target cell mapping, both along and across track. These deltas are used to compute the parameters for an “ellipse of influence” from a source cell to one or more target cells.
- The “ellipse of influence” is used both to compute which target cells are affected by a source cell – a bounding box to the ellipse of influence – and to compute a weighting factor for a weighted averaging of source cells per target cell. The weighting is defined in terms of the distance of the source cell center location to the target cell center (radius of the ellipse). Those source cells closer to the target cell are weighted more heavily than a simple linear cell-to-cell distance.
The “ellipse of influence” provides an important technique for calculating the area of influence, in the target grid
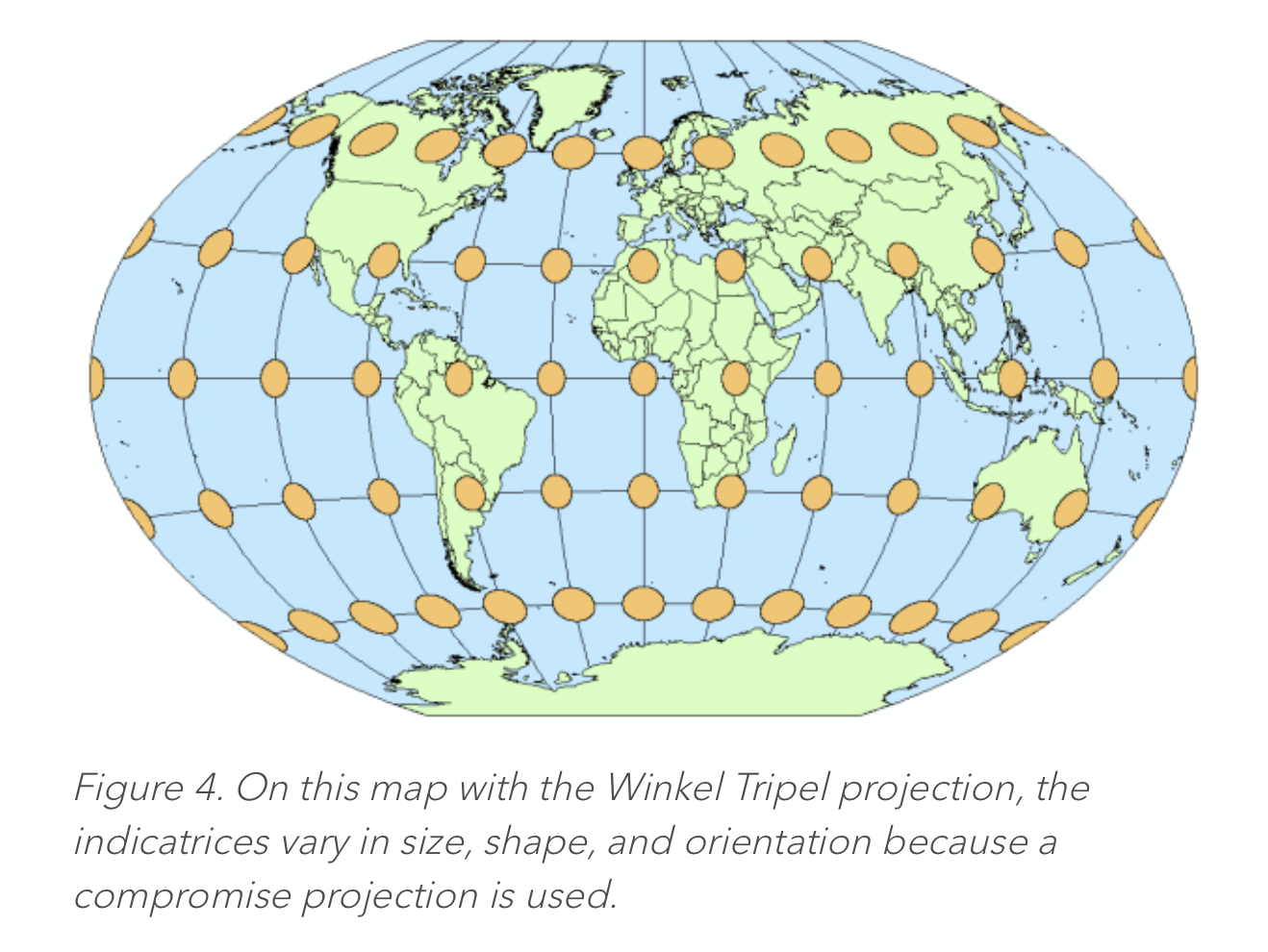
Expand title More details... This article provides a good introduction to Tissot's Indicatrix: https://www.esri.com/arcgis-blog/products/product/mapping/tissots-indicatrix-helps-illustrate-map-projection-distortion/
. It is an efficient way of finding target cells when forward projecting the source data grid to the output grid. This permits a reasonably efficient “forward navigation” approach, versus more typical reverse projection algorithms.
Anti-aliasing Filter
- An important but not always evident aspect of the EWA algorithm is a further adjustment of the weighting factors to implement a gaussian filter to the projection processing. The gaussian filter is important to minimizing the possible effects of aliasing and moiré effects when down-sampling a larger array of source data to a smaller set of target data … .
...
Overview
Content Tools