Earthdata Search Client Overview
Earthdata Search (https://search.earthdata.nasa.gov) is a modern web application allowing users to search, discover, visualize, refine, and access NASA Earth Observation data using ESDIS’ wide array of service offerings.
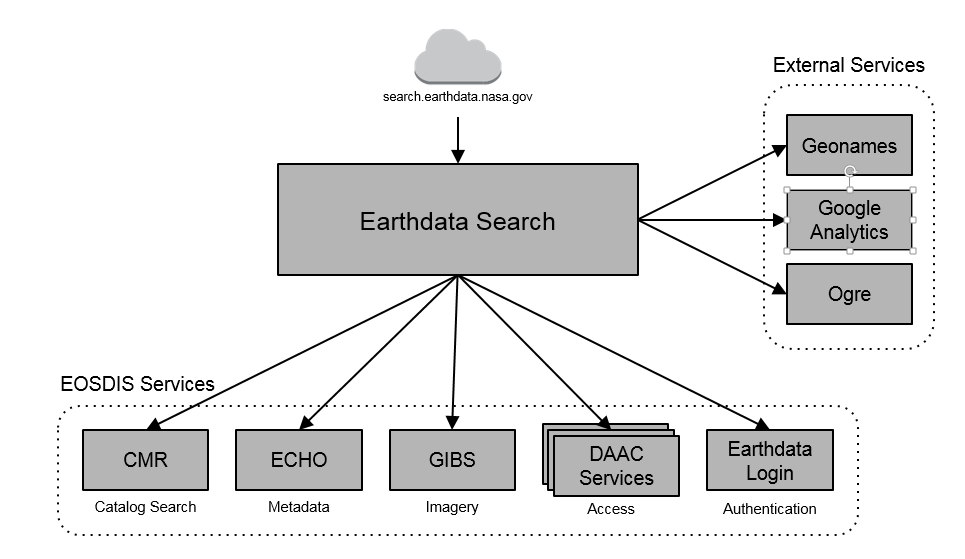
The Earthdata Search Client's goal in life is to allow users to easily discover earth science data. By nature of interfacing with the CMR, the Earthdata Search Client has access to all of the EOSDIS earth science data along with the international holdings previously only available through the Global Change Management Directory system.
System Architecture

The Earthdata Search Client is a Ruby on Rails application with a heavy JavaScript front end. It relies on a small postgres instance in order to save various pieces of information such as user's projects. To understand how this tool is built, below are some key decisions that were made during design and implementation.
Design Decisions with Rationale
•Knockout.js is used for the views and models. This allows a very simple observer-based system for managing change, speeding up development.
•Features with limited support (e.g. CWIC rendering) are placed in plugins separate from the main package. This keeps the overall footprint of the client manageable.
•Separate wrappers and adapters for the CMR API into small, well-defined areas and write tickets whenever we need to add to them. Eventually, use the CMR with limited transformation, directly from the browser, reducing overhead while improving accuracy.
Ranking of -ilities
Quality > Usability > Agility > Availability
•Quality – We value simple, lightweight client design to ensure that we are able to maintain a high quality user experience via low bug rates. We work with service and metadata owners to improve the stack we are built on.
•Usability – Design is a fist-class citizen in our process and we constantly solicit feedback and metrics to ensure we are meeting user needs.
•Agility – We incorporate new capabilities and respond to user and data provider needs.
•Availability – We maintain a zero-downtime application.
Architecture Patterns Used
•MVC – Model View Controller Separates concerns and allows varying uses of data
•Async Plugins – Reduces page size and improves performance
•MVVM (via Knockout.js) – Model View ViewModel allows for ightweight change observation
Key Trade-Offs
•Graceful degradation over Universal support – We prefer to assume collections will have the best possible feature support and degrade gracefully if they do not, rather than coding to the lowest common denominator. This acts as a carrot for better service support and high-quality metadata.
•Simplicity over Feature richness – New features, especially in rich web applications, come at a cost of higher cognitive load on users decreased performance, and higher maintenance costs. We treat new features with appropriate weight and design solutions to minimize it
•Dumb client over Smart - We prefer the CMR, having more complete information, provide us with required metadata and a clean search API, rather than attempting to clean up gaps by adding translations, thereby decreasing the weight of the client and improving the API for other clients.
•Data over Opinions - We value collecting metrics and using A/B testing to validate the feedback we are getting to ensure that it is in the best interest of our large user audience and not just representative of the opinion of one user.

